A price floor is a government or group imposed price control or limit on how low a price can be charged for a product good commodity or service.
Meaning of price floor in economics.
Price ceiling has been found to be of great importance in the house rent market.
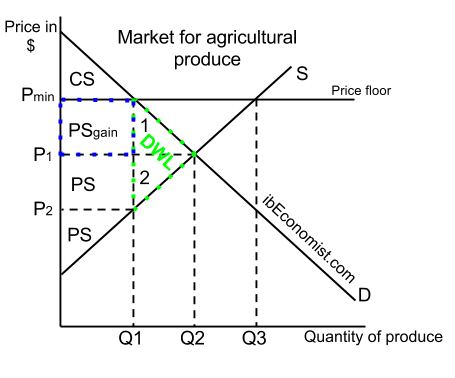
A price floor must be higher than the equilibrium price in order to be effective.
For example labor costs in the united states have a price floor of 7 25.
It has been found that higher price ceilings are ineffective.
It s generally applied to consumer staples.
A price ceiling is a maximum amount mandated by law that a seller can charge for a product or service.
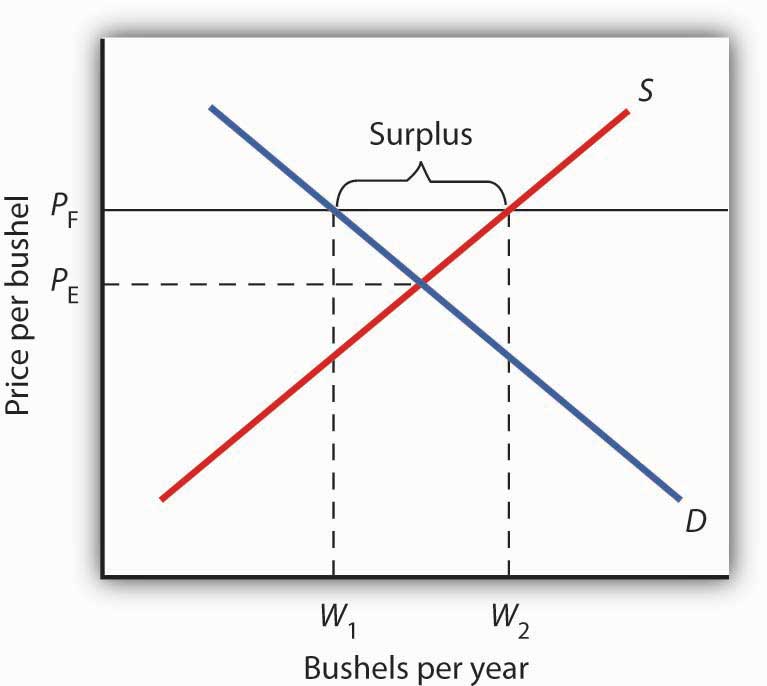
This graph shows a price floor at 3 00.
The equilibrium price commonly called the market price is the price where economic forces such as supply and demand are balanced and in the absence of external.
More specifically it is defined as an intervention to raise market prices if the government feels the price is too low.
Price floor is a situation when the price charged is more than or less than the equilibrium price determined by market forces of demand and supply.
However other price floors exist in any sector that the government is trying to protect such as agricultural goods or other sensitive industries.
Price floor in economics.
A price floor means that the price of a good or service cannot go lower than the regulated floor.
Prices below the price floor do not result in an.
A few crazy things start to happen when a price floor is set.
Price floor has been found to be of great importance in the labour wage market.
A price floor is the lowest amount at which a good or service may be sold and still function within the traditional supply and demand model.
First of all the price floor has raised the price above what it was at equilibrium so the demanders consumers aren t willing to buy as much.
A price floor or a minimum price is a regulatory tool used by the government.
A price floor is an established lower boundary on the price of a commodity in the market.
Definition examples.
Governments usually set up a price floor in order to ensure that the market price of a commodity does not fall below a level that would threaten the financial existence of producers of the commodity.
A minimum wage law is the most common and easily recognizable example of a price floor.
You ll notice that the price floor is above the equilibrium price which is 2 00 in this example.